Archived:PX4FMU Overview¶
Warning
ARCHIVED
The PX4FMU (v1) is end of life and is not generally available for purchase. This article is made available for existing users.
This page provides an overview of the Pixhawk Flight Management Unit.
Pixhawk (FMUv2) and PX4FMU (FMUv1)¶
The Pixhawk (FMUv2) single board autopilot evolved from the original “PX4 system”, which consists of the PX4FMU and various piggyback boards including the PX4IO and PX4IOAR.
The Pixhawk incorporates several additional features to provide extended capabilities for our ArduPilot flight system.
A connector diagram of the Pixhawk is shown below, but Go to this link for full information on the Pixhawk
The PX4FMU/PX4IO (FMUv1) Flight Management System Includes:¶
The PX4-FMU (Flight Management Unit).
A powerful Cortex M4F micro-controller and flash memory for controlling flight and communications.
A socket for a plug in SD memory card.
A 3 axis gyro for determining orientation.
A 3 axis Accelerometer for determining outside influences.
A compass (magnetometer).
A barometric pressure sensor for determining altitude.
A connection for an externally mountable UBLOX LEA GPS for determining absolute position.
Stackable board interconnections for adding various peripheral boards.
Communications interfaces for USB, JTAG and Serial connections.
Connections for PPM-SUM RC radio input and servo outputs.
The PX4-IO (Input Output) Board.
Contains its own on board micro-controller and stacks with the FMU.
Direct battery input power supply.
8 High speed servo PWM outputs.
Futaba SBUS or PPM-SUM serial servo output.
A variety of PPM-SUM / SBUS input connectors.
Two user assignable relays, two 1/2 amp 5 volt outputs and an analog input port.
The PX4FLOW Smart (Optical Flow) Camera.
Specialized downward pointing camera module that uses ground texture and features to determine aircraft motion over the ground.
The PX4FLOW has the same powerful Cortex M4F micro-controller as is used in the PX4FMU.
The built in micro-controller performs on board automated binned pixel image analysis to determine motion relative to ground.
A built in 3 axis gyro enables automatic compensation for variance in aircraft tilt angle.
The PX4-IOAR Quad Carrier is a specialized interface board for the Parrot AR.Drone.
The PX4FMU circuit board comes preassembled and ready to load the firmware for your airframe using the Mission Planner.
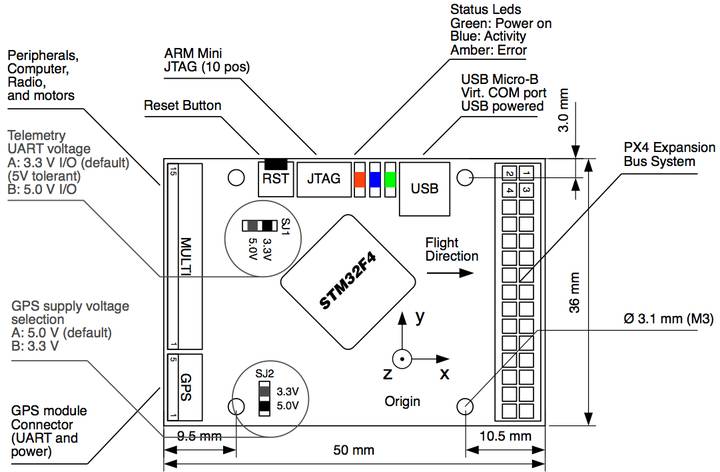
Detailed Description¶
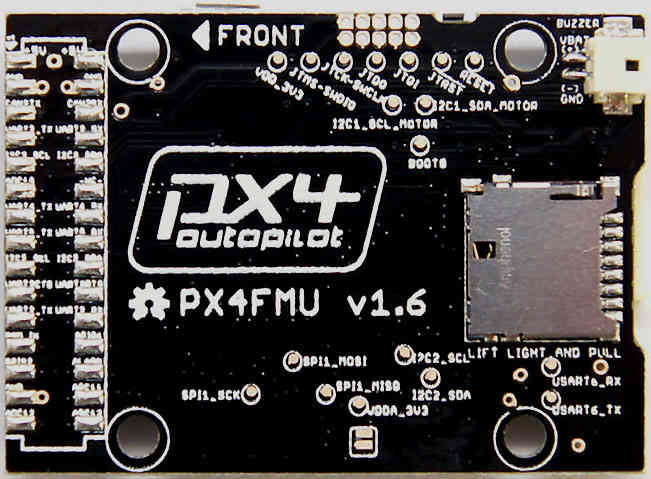
The Back of the PX4FMU board showing the SD card carrier and buzzer socket:
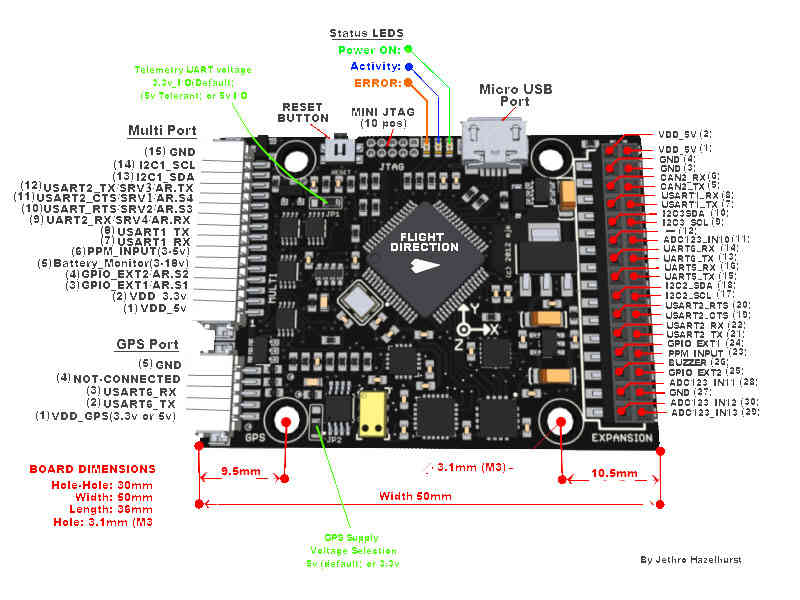
PX4FMU Connector diagram¶
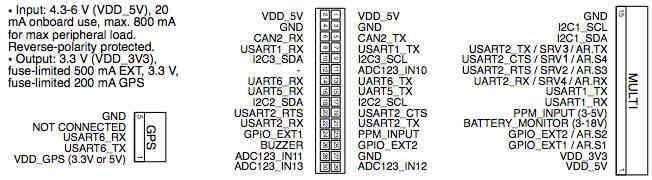
Analog and digital pins¶
This section lists what pins (analog and digital) are available on the PX4FMU.
PX4v1 Analog inputs¶
The PX4FMUv1 has the following “available” Analog input port pins which may be put to a variety of uses.
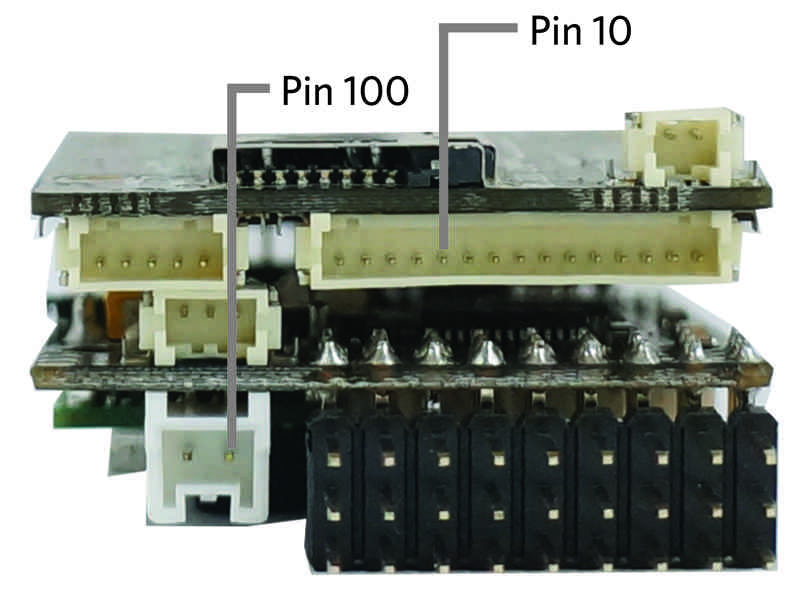
Pin 10 (High voltage analog pin):
FMU battery voltage measured on pin 5 of the 15 pin multi-connector on the end of the FMU board. It has 5.7:1 scaling, allowing it to measure up to 18.8V.
Located on pin 5 of the DF13 15 pin “multi-connector” of the PX4FMU board.
This pin can accept up to 18.6 volts. (You can add an additional resistor divider and set the scaling appropriately for higher voltages).
With the Advanced Parameter VOLT_DIVIDER set to 1 voltage can be read directly.
For old releases VOLT_DIVIDER needed to be set to 5.66 for direct voltage scaling.
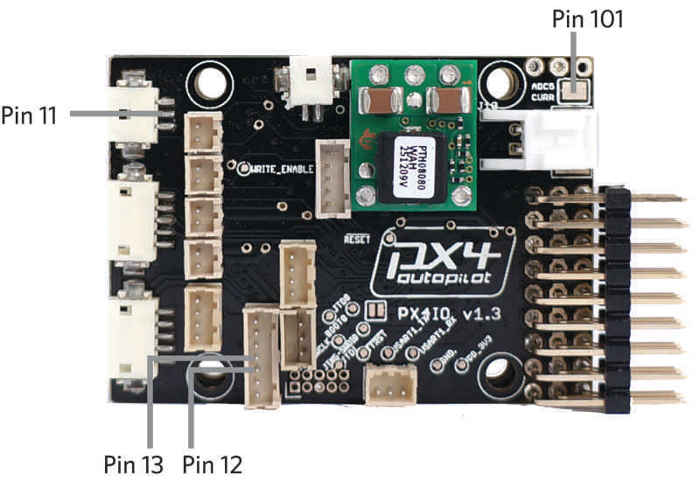
Pin 11 (Analog airspeed input pin)
Located on pin 2 of the 3 pin “FMU-PRS” DF13 connector on the PX4IO board.
Generally used in Plane for the Air Speed Sensor with VCC on pin 1, Sensor on pin 2 and Ground on pin 3.
Plane Advanced Parameter: ASPD_PIN set to 11.
This pin is directly connected to the ADC on the PX4FMU.
This pin can accept up to 6.6 volts (it has an internal voltage divider with 2:1 scaling).
Pin 12 (Analog 2 input)
Located on pin 3 of the “FMU-SPI” port on the PX4IO board.
Commonly used for Sonar
Copter and Rover Advanced Parameter: SONAR_PIN set to 12
This pin is directly connected to the ADC on the PX4FMU.
This pin can accept up to 3.3 volts.
Pin 13 (Analog 3 input)
Located on pin 4 of the “FMU-SPI” port on the PX4IO board.
Commonly used for Sonar 2 in dual Sonar installations.
Rover Advanced Parameter: SONAR2_PIN set to 13
This pin is directly connected to the ADC on the PX4FMU.
This pin can accept up to 3.3 volts.
Pin 100 (Battery voltage measured on the power connector on the IO board. Limit is 18V).
A virtual analog input pin for voltage of a battery connected to the 6V to 18V input of the PX4IO voltage regulator.
This is the normal pin to use for LiPo monitoring on the PX4IO.
If using this pin then set VOLT_DIVIDER to 1 for correct battery voltage reading.
Virtual “pin” 100’s input comes only from the battery power in jack on the PX4IO board.
This “pin” is not brought out for separate user access.
This pin is separate from the Pin 10 high voltage analog pin on the PX4FMU listed above which can also be used as a battery voltage monitor.
Pin 101: Battery current measured on the pin next to the power connector on the IO board.
A virtual analog input pin for a battery current sensor connected to the “current” pin next to the power connector on the PX4IO.
Warning
- You need to be careful
to use a current sensor that will not provide over 3.3V as too high a voltage on this pin can cause the PX4IO to reset.
For use with a current sensor, a 0.1uF capacitor between this pin and ground will help reduce “noise”.
PX4v1 Digital outputs¶
The PX4V1 digital output pins come in two types, one is pins that give 5V when on and 0V when off, and the other are ‘relay’ pins which provide low resistance when on and high resistance when off.
Pin 111: FMU Relay pin 1
Pin 112: FMU Relay pin 2
Pin 113: IO Relay pin 1
Pin 114: IO Relay pin 2
Pin 115: IO digital accessory pin 1
Pin 116: IO digital accessory pin 2
Copter wiring (diagram and instructions)¶
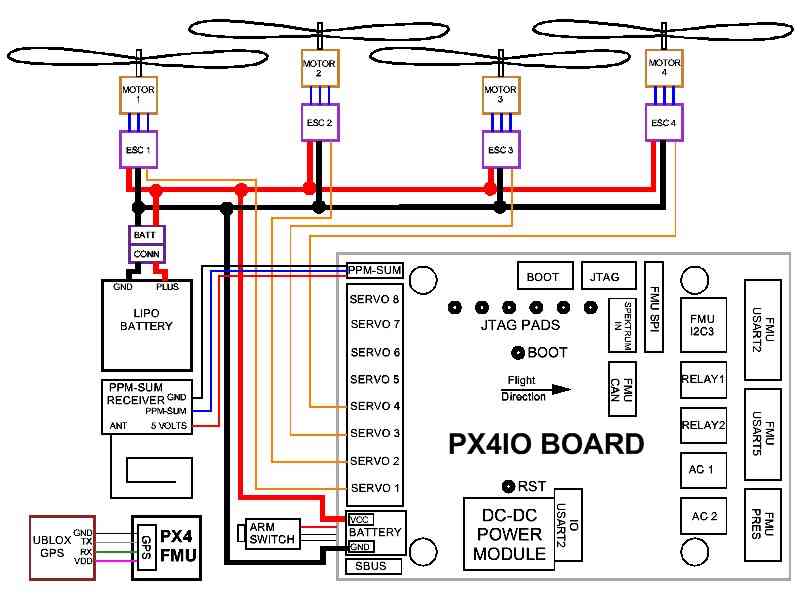
Wire the PX4-IO board.
The PX4IO board has a built in Power Supply which can connect to up to 18 volts.
Insert the white PAP-02-VS 2 pin connector with the black and red wires coming out of it into the mating power connector you soldered in previously on the PX4IO board.
Battery Plus is the(red wire) and should be soldered to your battery red power lead / connector.
Battery Ground is the(black wire) and should be soldered to your battery black battery (Ground) lead / connector.
The main power inputs of your ESC’s will also need to connect to these wires and to a battery connector.
A Power Distribution board can also be used.
Connect your PPM-Sum RC receiver’s 3 wire cable to the end of the 9 x 3 angle connector that is nearest the edge of the PX4IO board with the signal wire furthest from the board and the ground closest to the board.
Wire the PX4FMU boards servo out signals to your ESC control inputs.
Run the Signal wires ONLY from the ESCs to the 3 x 9 Servo Connector on the PX4IO board.
The PX4IO board connector for Motor 1 is at the edge of the connector next to the Battery power in wires.
Insert the Motor ESC wires arranged progressively from that edge, (1,2,3,4,etc) for 2 to 8 motors depending on your copter type.
You can put the ESC Signal wires into a single inline connector with the correct number of pins for your copter.
The ESC Signal Wires / connector should be plugged into the top row (furthest from the board) of the PX4IO boards 3 x 9 Servo Connector.
Note, the cable that is supplied in the plastic envelope with the UBLOX GPS which has white 6 pin connectors on both ends is not the correct cable for the PX4FMU board.
The correct longer GPS cable is provided in a separate envelope and has a 5 pin “beige” connector on one end and a 6 pin white connector on the other end.
Plug the correct GPS cable’s white 6 pin connector into the 6 pin socket on the GPS.
Plug the beige 5 pin connector into the PX4FMU board’s 5 pin GPS socket which is next to the 15 pin DF13 Mini connector.
Plug the 2 pin connector attached to the lead supplied with the buzzer into the buzzer socket on the side of the PX4FMU board that has the SD card holder on it.
Connect the “Arming Switch” to the Arming switch connector on the PX4IO board on the opposite side of the board from the Battery pads.