When Problems Arise¶
ArduPilot, is extremely capable and flexible. But with high performance and flexibility comes a lot of configurations, parameters, and complexity.
This WIKI documentation attempts to reduce the effort of configuring and operating your ArduPilot based vehicle by providing as much accurate information on configuration, parameters, and operating modes as possible, and is continuously being updated as new releases occur or areas needing further explanation arise. Your assistance in that effort is welcomed and solicited. See Wiki Editing Guide
Note
Enabling and using the logging capability of ArduPilot is usually a key requirement when seeking assistance from other in diagnosing issues that you cannot resolve yourself by following the suggestions below.
What to do if you have an issue¶
Make sure you have followed the vehicle’s “First Time Setup” and “First Flight/Drive” Sections and carefully read the provided documentation. If dealing with advanced configuration or hardware options, thoroughly read the appropriate documentation.
If this does not help you resolve the issue, then seek help on the Discuss Forum section appropriate to your vehicle or ground station. Do not enter issues on the GitHub software repositories unless it has been confirmed as an actual issue in the code or documentation. Support will be given in the appropriate Discuss Forum.
Having a dataflash log will help you, or someone helping you, to diagnose the issue.
Note
WatchDog resets (“WDG:”) should be reported on this page , Internal Errors (“Internal Error:”) should be reported here
Vehicle Will Not Arm¶
See Pre-Arm Safety Checks. Do not disable arming checks except for bench setup testing. Doing so puts your vehicle at risk for a crash. Always track down the reason why a pre-arm check failure is occurring and correct it before operating the vehicle!
Interference issues on Electric Vehicles¶
Routing high current carrying wiring for motors in close proximity to ESCs or Servo Control wiring can result in interference with those peripherals controls due to electromagnetic coupling. Below is a video of aileron servos having their operation disrupted due to induced noise from adjacent motor high current wiring:
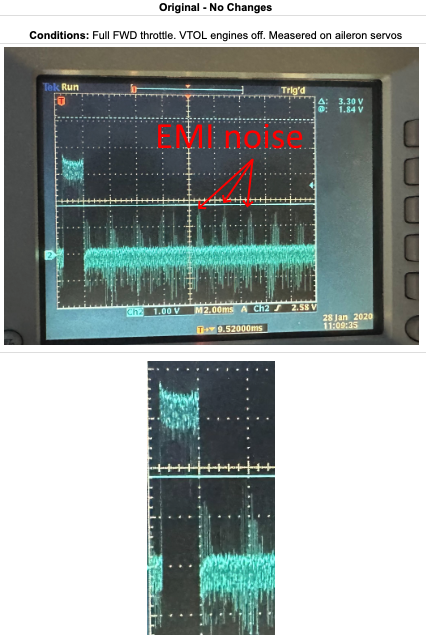
This can be resolved by separating the power conducting and the signaling wiring by several inches or by using a more noise tolerant servo such as DroneCAN servos.
See also ESC Signalling Issues for similar issues with ESCs.
Copter Common Problems¶
new copter flips immediately upon take-off. This is usually caused by the motor order being incorrect or spinning in the wrong direction or using an incorrect propeller (clockwise vs counter-clockwise). Check the rc connections for your autopilot.
copter wobbles on roll or pitch axis. This usually means the Rate P values are incorrect. See Tuning section for some hints as to how to adjust these gains.
copter wobbles when descending quickly. This is caused by the copter falling through its own prop wash and is nearly impossible to tune out although raising the Rate Roll/Pitch P values may help.
copter yaws right or left 15degrees on take-off. Some motors may not be straight or the ESCs have not been calibrated.
copter always tends to fly in one direction even in a windless environment. Try SaveTrim or AutoTrim to level the copter.
copter climbs rapidly even if the pilot pulls the throttle down. This is likely caused by high vibrations. See https://ardupilot.org/copter/docs/common-vibration-damping.html for methods to improve vibration isolation.
occasional twitches in roll or pitch. Normally caused by some kind of interference on the receiver (for example FPV equipment placed too close to the receiver) or by ESC problems that may be resolved by calibrating them.
sudden flips during flight. This is nearly always caused by mechanical failures of the motor or ESCs.
Free RAM issues¶
During initialization, it is possible for some features/subsystems to fail to get enough RAM allocated. Sometimes this will be announced such as in the case of insufficient memory to start a LUA script: “Scripting requires a larger minimum stack size”, or for terrain: “Terrain: Allocation failed”, etc. Also, insufficient free memory can result in compass calibration failing or MAVftp not initializing. See RAM Limitations for more information.
H7 AutoPilot Will Not Initialize¶
AutoPilots utilizing the H7 series of processors can, on rare occasions, get into a state where they will no longer complete initialization. Symptoms are: never exiting the bootloader (rapidly flashing led right after power application never stops) or the autopilot freezes during initialization, and connection to it is impossible.
It is believed that this may be a memory corruption problem which can be caused by interrupting a flash memory write (as when changing parameters). Unfortunately, due to the processor’s architecture, there is no way in the firmware to correct this automatically. If the autopilot seems “bricked”, try this to completely reset the autopilot to a fully un-programmed state. This should allow the firmware to be installed and the corruption issue resolved.
First, program the entire 2MB flash space with zeros by loading this file which contains all zero data. Use the instructions here but use the above file.
Next, download the ArduPilot bootloader for your AutoPilot from here. Then repeat the above step using that bootloader file. This will place the bootloader on the autopilot. Cycle the power on the autopilot. At this point it will power up and remain in the bootloader until operational firmware is installed.
Finally, use Mission Planner’s SETUP/Install Firmware tab or the Uploader python script, to load the desired ArduPilot firmware revision.
This should resolve issues caused by memory corruption and normal operation will resume.