Using Python Scripts in Mission Planner¶
One of the cool features of the Mission Planner is that it can run Python scripts, which is an easy way to extend the functionality of the program beyond its built-in functions. It can also enable integration easily with other dlls and modules far beyond the original scope of the Mission Planner.
Overview¶
You can easily program your UAV to do anything, from robotic acrobatics to just script-driven missions. Python 2.x is currently supported, up to 2.7 (Mission Planner uses an implementation of IronPython internally)
Aside from the regular Python commands, these are the special Mission Planner commands you can use:
cs.VARIABLENAME = currentstate
Any variable on the status tab in the planner can be used.
Script.METHODNAME(...)
options are
Script.Sleep(ms)Script.ChangeParam(name,value)Script.GetParam(name)Script.ChangeMode(mode)(same as displayed in mode setup screen ‘AUTO’)>
Script.WaitFor(string,timeout)Script.SendRC(channel,pwm,sendnow)
Here’s an example, which tells a multicopter to do a roll in the air!
print 'Start Script'
for chan in range(1,9):
Script.SendRC(chan,1500,False)
Script.SendRC(3,Script.GetParam('RC3_MIN'),True)
Script.Sleep(5000)
while cs.lat == 0:
print 'Waiting for GPS'
Script.Sleep(1000)
print 'Got GPS'
jo = 10 * 13
print jo
Script.SendRC(3,1000,False)
Script.SendRC(4,2000,True)
cs.messages.Clear()
Script.WaitFor('ARMING MOTORS',30000)
Script.SendRC(4,1500,True)
print 'Motors Armed!'
Script.SendRC(3,1700,True)
while cs.alt < 50:
Script.Sleep(50)
Script.SendRC(5,2000,True) # acro
Script.SendRC(1,2000,False) # roll
Script.SendRC(3,1370,True) # throttle
while cs.roll > -45: # top half 0 - 180
Script.Sleep(5)
while cs.roll < -45: # -180 - -45
Script.Sleep(5)
Script.SendRC(5,1500,False) # stabilize
Script.SendRC(1,1500,True) # level roll
Script.Sleep(2000) # 2 sec to stabilize
Script.SendRC(3,1300,True) # throttle back to land
thro = 1350 # will descend
while cs.alt > 0.1:
Script.Sleep(300)
Script.SendRC(3,1000,False)
Script.SendRC(4,1000,True)
Script.WaitFor('DISARMING MOTORS',30000)
Script.SendRC(4,1500,True)
print 'Roll complete'
Classes Exposed by Mission Planner to Python¶
Mission Planner exposes classes using the following code:
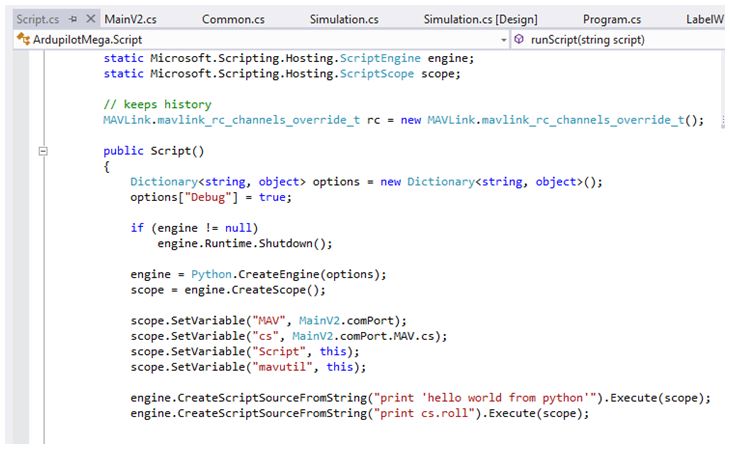
Linking classes into python¶
scope.SetVariable(Variablename, ClassInstance);
That the following classes are exposed:
scope.SetVariable("MAV", MainV2.comPort);scope.SetVariable("cs", MainV2.comPort.MAV.cs);scope.SetVariable("Script", this);scope.SetVariable("mavutil", this);
This is where you can add your own classes. For now lets us explore the important methods and properties you can use into your script using these classes.
Class Name: Script.cs
Python Variable: Script , mavutil
Method |
Description |
bool ChangeParam (string param, float value) |
|
Float GetParam (string param) |
|
bool ChangeMode (string mode) |
Changes flying mode |
bool SendRC (int channel, ushort pwm, bool sendnow) |
Send Chxout values. |
Class Name: CurrentState.cs
Python Variable: cs
Method |
Type |
Description |
roll |
float |
Roll (deg) |
pitch |
float |
Pitch (deg) |
yaw |
float |
Yaw (deg) |
lat |
float |
Latitude (deg) |
lng |
float |
Longitude (deg) |
groundcourse |
float |
Ground Course (deg) |
alt |
float |
Altitude (dist) |
altoffsethome |
float |
Altitude Home Offset (dist) |
gpsstatus |
float |
GPS Status |
gpshdop |
float |
GPS HDOP |
satcount |
float |
Satellite Count |
altd100 |
float |
Altitude / 100 |
altd1000 |
float |
Altitude / 1000 |
airspeed |
float |
Airspeed (speed) |
targetairspeed |
float |
Airspeed Target (speed) |
groundspeed |
float |
Ground Speed (speed) |
verticalspeed |
float |
Vertical Speed (speed) |
wind_dir |
float |
Wind Direction (deg) |
wind_vel |
float |
Wind Velocity (speed) |
ax, ay, az |
float |
Acceleration Values in x,y,z |
gx, gy, gz |
float |
Gyro Values in x,y,z |
mx, my, mz |
float |
Mag Values in x,y,z |
failsafe |
bool |
Fail Safe Active or Not |
rxrssi |
float |
|
chx1in, chx2in, …. chx8in |
float |
Input Channels from 1 to 8 |
ch1out, chx2out, …. chx8out |
float |
Output Channel form 1 to 8 |
nav_roll |
float |
Roll Target (deg) |
nav_pitch |
float |
Pitch Target (deg) |
nav_bearing |
float |
Bearing target (deg) |
target_bearing |
float |
Bearing Target (deg) |
wp_dist |
float |
Distance to Next Waypoint (dist) |
alt_error |
float |
Altitude Error (dist) |
ber_error |
float |
Bearing Error (dist) |
aspd_error |
float |
Airspeed Error (speed) |
wpno |
float |
Flying Mode |
mode |
String |
Flying Mode |
dimbrate |
float |
Climb Rate (speed) |
tot |
int |
Time over target (sec) |
distTraveled |
float |
Distance Traveled (dist) |
timeInAir |
float |
Time in Air (sec) |
turnrate |
float |
Turn Rate (speed) |
radius |
float |
Turn Radius (dist) |
battery_voltage |
float |
Battery Voltage (volt) |
battery_remaining |
float |
Battery Remaining (%) |
current |
float |
battery Current (Amps) |
HomeAlt |
float |
|
DistToHome |
float |
Absolute Pressure Value |
press_abs |
float |
Absolute Pressure Value |
sonarrange |
float |
Sonar Range (meters) |
sonarVoltage |
float |
Sonar Voltage (volt) |
armed |
bool |
True if Armed |
Please note that although these properties are read/write howvever writing to some of them can corrupt the status. Use methods from Script class to control the vehicle. for example use Script.ChangeMode(xmode) rather than cs.mode = xmode.
Class Name: MavLink.cs
Python Variable: MAV
Method |
Description |
bool setParam (string paramname, float value) |
Same as Script.ChangeParam() |
bool doARM (bool armit) |
BE CAREFUL when using it. |
byte getWPCount ( ) |
Gets Waypoints Count. |
Using CPython Standard Libraries¶
You can import standard libraries from your regular Python 2.x folders by adding this line to top of your script (replacing “c:\python27\lib” with whatever the folder is on your drive):
import sys
sys.path.append(r"c:\python27\lib")
Here, for example, we’re importing the serial, os, and threading libraries, which are in two folders in a typical Python 2.7 installation. Appending the specific folder paths for those three libraries first allows us to import them with the next “import” command:
import sys
sys.path.append(r"c:\Python27\Lib\site-packages")
sys.path.append(r"c:\Python27\Lib")
import serial, os, threading