Rebasing: keeping your code up to date¶
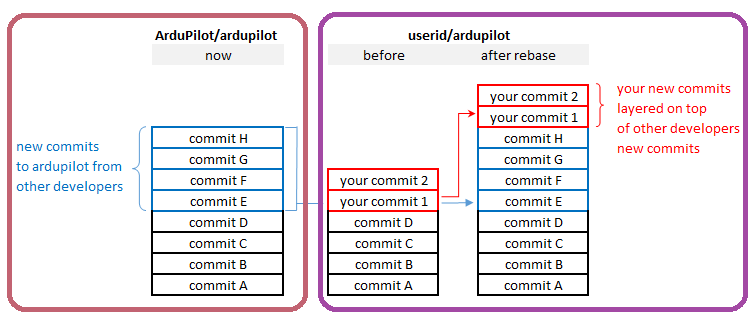
As you develop, ArduPilot’s master branch is likely to be updated with “commits” from other developers. You should keep your local branches and fork up to date so that you are working with the latest code and to make it easier for maintainers to eventually merge your changes to ArduPilot’s master branch.
In particular it is best to keep your local repo and forked repo’s master branches up-to-date with ArduPilot’s master branch.
“Rebasing” allows you to update a branch from ArduPilot’s master branch and then re-apply any changes you may have made to the branch.
The following commands can be entered directly into a Linux/OSX terminal or if using Windows, launch the “Git Shell” or “Git Bash” utility that should already be installed.
Navigate to your ardupilot git repository.
cd <ardupilot-path>
Starting from here we will assume that you want to rebase your topic-branch on ArduPilot master branch. This process is the same for the master branch, just replace topic-branch with master. Ensure you are looking at your master branch or the branch that you want to rebase.
git checkout topic-branch git submodule update --init --recursive
If you want to create a new branch to work on which you would like to rebase on top of the ArduPilot master branch,
git checkout -b topic-branch git submodule update --init --recursive
Ensure your repository is connected to the upstream repository you forked from.
git remote add upstream https://github.com/ArduPilot/ardupilot.git
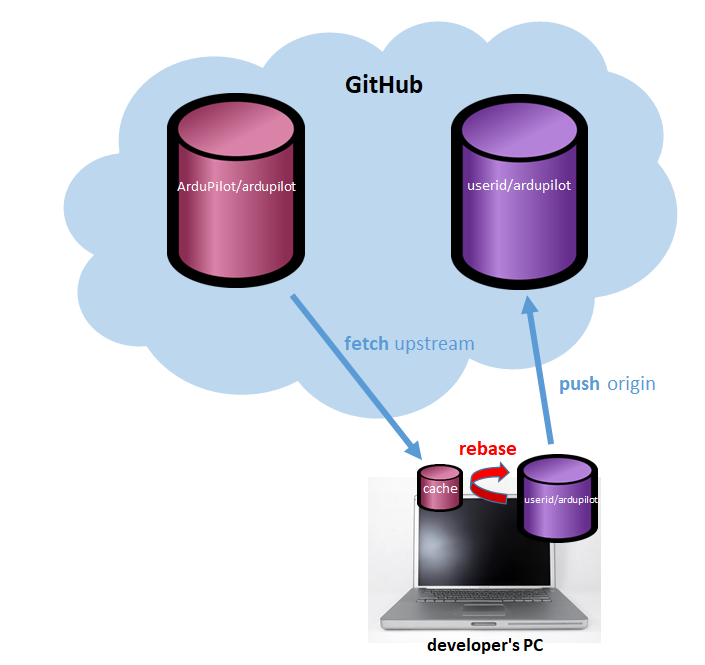
Fetch changes from the upstream repository (this simply downloads changes into a local cache, it will not overwrite or modify your changes in any way). If you are rebasing your branch on your own fork’s master branch, replace upstream with origin
git fetch upstream git submodule update --init --recursive
Rebase your current branch from the upstream’s master branch.
git rebase upstream/master
Initialize and update your local repo’s submodules
git submodule update --init --recursive
Check that the rebase was successfull. Using cmdline (
git log --oneline --decorate --all --graph, type q to exit) or a GUI tool like gitk, sourcetree, etc. Your commits should appear on top of ArduPilot master lastest commit, like show on previous picture.Now push the updated branch to your github repository
git push origin topic-branch
When things go wrong¶
The rebase step (step 5) above may fail for a few reasons:
there are uncomitted changes to files in your local repo’s branch. Stage and commit these changes and then try again.
there are merge conflicts meaning that another developer has changed the same lines of code as your new commits have changed. There are two choices
abort the rebase which will restore your branch to how it was before you began the rebase,
git rebase --abort. If you are happy to throw away your new commits in your local repo’s branch you can “reset” your branch so that it looks exactly like upstream master usinggit reset --hard upstream/master.user a merge tool like TortoiseGit to resolve the mergeconflict and then continue with the rebase using
git rebase --continue
The submodule update (step 6) occasionally fails if new submodules have been added. git submodule init usually resolves this.
The push step (step 7) above may fail if your fork’s branch has already been updated previously. You can “force” the push using git push -f which will overwrite your github fork’s branch to look like your local repo’s branch. It will also fail if the topic-branch does not already exist in your remote repository. In that case use
git push -u origin topic-branch
to create the branch there and have your local topic-branch track it.