Building Mission Planner with Visual Studio¶
Introduction¶
Mission Planner (MP) is an open source ground station developed in C# primarily for use on Windows/linux computers (although it can be run on Mac and Linux using mono). This is the most commonly used ground station as it provides the most complete functionality for vehicle setup as well as pre-flight mission planner, in-flight monitoring and post flight log file analysis.
This page provides instructions on how you can build the Mission Planner software on your own machine using MS Visual Studio which may be useful if you wish to make changes for your own use or improvements for the community. Building the mission planner may also help as a guide in case you plan to build your own custom ground station development.
Some warnings before you dive in:
Use your modified / complied version of Mission Planner at your own risk.
Mission Planner is a very complex including and making changes is not for the faint of heart. Here are the basic skills you will need to make reasonable progress with MP changes:
C# programming skills and experience (at least or C++ experience).
Experience with Microsoft Visual Studio (VS) development environment. MP is not the application to begin learning VS.
Experience using Windows API (Application programming Interface)
Including understanding of streams, processes, threads.
Support for Visual Studio, programming in C# and Windows API may not be forthcoming from the DIY Drones community. You will need to get that support from other sources.
System Requirements¶
Here is what you will need.
Windows 10 or later (Windows 7 and older versions are not compatible).
Sufficient disk space (arround 20GB for VS installation), memory, processor power to comfortably run Visual Studio.
An Internet connection.
Visual Studio (NOT VSCode), at least version 2022. The Community Edition suffices.
Install Visual Studio¶
Begin by installing Microsoft Visual Studio and configuring it for your Windows system. Follow these steps:
Download Visual Studio: Visit the Microsoft Visual Studio download page and download the Community Edition by default.
Customize Installation: Visual Studio is a comprehensive suite with built-in Git support, but it can be overwhelming due to its complexity. To streamline the installation process, consider these steps: - Access “More” in the Visual Studio installer. - Choose “Import configuration.” - Import the provided configuration file: vs2022.vsconfig.
By following these instructions, you will have the necessary components installed and ready for Mission Planner development.
VSCode¶
While Visual Studio Code with the C# plugin can parse the code, please note that it cannot build Mission Planner at this time.
After your VS installation is complete:¶
You should be able to use Git from the IDE. Clone Mission Planner source code to get the full code.
Building the MissionPlanner¶
To build the code, follow these steps:
Open MissionPlanner.sln file with Visual Studio
From the “Build” menu, select “Build MissionPlanner”
By default, Visual Studio will compile all projects and their dependencies as part of a build process.
Non Windows building¶
Building Mission Planner on other systems isn’t support currently.
Building the SimpleExample¶
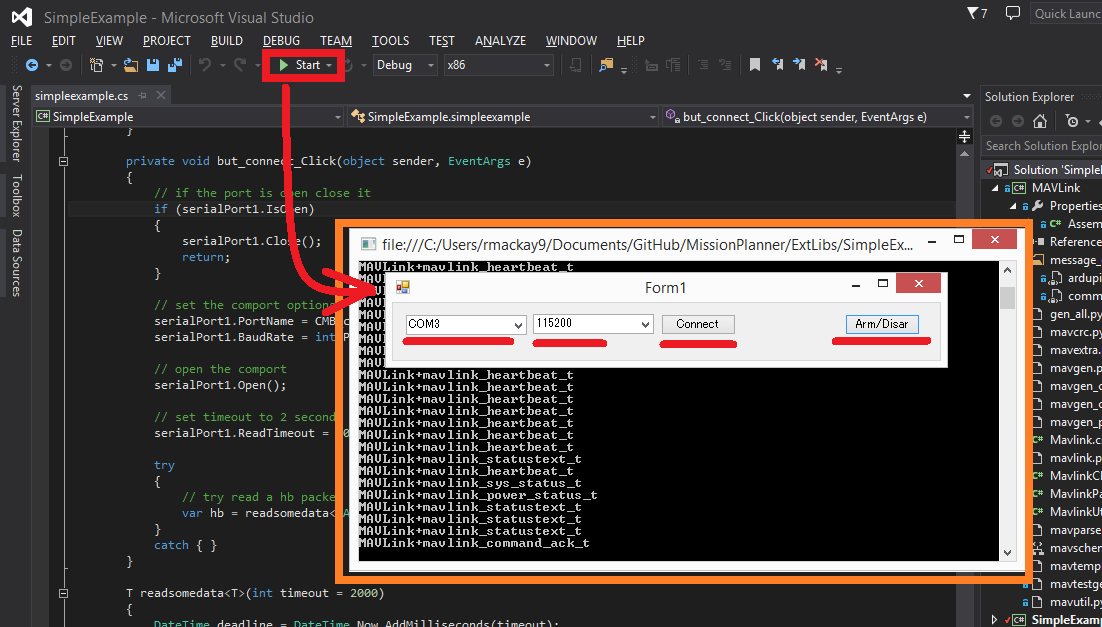
The “SimpleExample” solution is available as a near minimal application to demonstrate how a C# program can connect to a vehicle and cause it to arm or disarm. This example has many fewer dependencies than the full Mission Planner and is simpler to build and understand.
Open the solution from Visual Studio by selecting File >> Open >> Project/Solution, and in the MissionPlanner code directory select ExtLibs / SimpleExample.sln ( close the MissionPlanner solution first if you have that open )
Ensure the program can be build successfully by selecting Build >> Build Solution.
After first checking that you can connect to your flight controller and arm it with the regular mission planner, disconnect the regular Mission Planner and then press “Start” to run the application in debug mode. When the “Form1” pops up, select the COM port, the baud rate (probably 115200) and press Connect. If it successfully connects, press Arm/Disarm to attempt to arm the vehicle.
Note
there is no error checking in the application if it fails to connect it
Warning
Following instructions are deprecated and were only kept for example. There are probably not working and need update.
Editing and Debugging Mission Planner (and Other Tips)¶
Editing and debugging details are beyond the scope of this Wiki. Debugging may result in some warnings. You should learn what they mean and take the necessary steps to resolve them if that is the case. Here is a simple debugging example to get you started.
Do not (yet) connect your AutoPilot Hardware ( CubeOrange, etc. ) to the compiled version of MP. You must first copy some .xml files to the bin/debug folder. See details below.
First be sure VS is configured for debug (versus release) Set this in the top menu tools area or the configuration manager.
Select menu DEBUG, Start Debugging. (Or, press F5). Mission Planner should run as you normally see it. However, some important configuration files are missing so connection to the AutoPilot Hardware ( eg CubeOrange, etc ) is not recommended at this time.
If after “Start Debugging” the program loading hangs in the splash screen and you see this message: “Managed Debugging Assistant ‘LoaderLock’ has detected a problem …… “’ and/or the debugger has paused at the line Application.Run(new MainV2()); in ArduPilotMega.Program then do this:
Select [Debug], [Exceptions]. Expand the [Managed Debugging Assistants]. Uncheck the ‘Loader Lock’ check box
Close MP. (Or, select menu DEBUG, Stop Debugging in VS).
Next you can try setting a break point.
Expand the MissionPlanner project in the VS Solution Explorer so you see the objects included.
Scroll down to MainV2.cs, right click that object and select View Code.
In the code window for MainV2.cs, scroll down to the line “public MainV2” then to one of the first code lines after that ( currently it is a log.Info(”…”); line ) .
Click in front of that line (In the dark gray bar on the left) to set a break point (red circle).
Start Debugging (press F5).
You will see the normal MP start up windows up to the Splash window but then it will stop running. You have hit the break point. Visual Studio will show the code and the break point will be highlighted. Note that you cannot move the splash screen so you may need to relocate the VS window to see the break point.
Move your mouse over different variables and objects in the code. You will see the current values of many or the items.
Press F5 and Mission Planner will continue loading.
Further details on editing and debugging are left to the user.
Using your modified Mission Planner¶
If you make changes to Mission Planner, you will probably want to make use of your version. Here we will give you some preliminary information to do that. You can use your local compiled version but the compiled output files are located in different places in VS and some additional steps are required. There are configuration files specific to your installation of Mission Planner that are not included in the Git hub download that are only provided in the Mission Planner installation package. You will need to copy these to the correct area in the folder you are using for the Visual Studio project. Here are the steps that will get you started.
Use your modified complied version of Mission Planner at your own risk.
- These steps assume VS is in the debug configuration. [editors]
Details when in Release mode could be added [/editors]
In order for your VS version of MP to function with ArduPilot connected, you will need to copy several files from the folder where MP is installed (C:\Program Files (x86)\APM Planner or C:\Program Files\APM Planner) to the folder where your VS project compiled output is located.
Todo
editors: This needs to be made more accurate which files are needed, why etc.
Copy (don’t move) all xml files (I.E. files with the extension .xml) from the root folder of the MP installation (C:\Program Files\APM Planner) to the bin/Debug folder in the folder where your Visual Studio Mission Planner solution is stored. (the Git hub clone folder). This will setup your compiled version to match the current configuration of your AutoPilot (copter versus plane, other options, etc)
I.E, if you solution is in folder MPGitClone, then copy the .xml files to MPGitClone\bin\Debug. Some will copy without notice, but some will ask you if you want to replace the existing file. Replacing all seems to work but you should investigate further to be sure you can use MP for real life situations before you do so.
If you build Mission Planner in Release mode, then the files should be copied to the bin/Release folder. This has not been tested at this time.
Here are some other tips:
Location of Logs saved when using your version will be in the /bin/Debug or bin/Release folder. This can be changed with Mission Planner 1.2.63 and later versions.
If you want to make a shortcut to run your version of Mission Planner without running Visual Studio, create the shortcut to point to the program ArduPilotMegaPlanner10.exe in the bin/Debug or bin/Release sub folders.
At this point your local version of MP should be working. You should be able to connect to your ArduPilot FCU, Flight Data including status should work, Configuration should bring up you ArduPilot parameters, Terminal should work including saving and browsing logs. Flight Planner should also work. As mentioned before, use your modified version at your own risk.
Submitting your changes for inclusion in Master¶
Generally the advice is the same as for the ArduPilot flight code (instructions here) but here is a very short summary of the steps:
Sign up a member of Git hub
Create a personal Fork of the Mission Planner by going to https://github.com/ArduPilot/MissionPlanner and click on Fork (Upper right corner area) This creates a copy (fork) of Mission Planner files in your Git Hub account.
Clone your personal repo (created with the Fork above) to your PC
Create a new branch in your repo and commit your changes and push these back to GitHub (these will only go into your repo on GitHub).
Use the GitHub web page to create a Pull Request from your branch
The owner of Mission Planner (Michael Oborne) will receive an email notifying him of your Pull Request. He will most likely review, provide feedback and if he accepts the commit it will be added to master.