Building for Bebop 2¶
These instructions explain how to use ArduPilot for the Bebop2 on a Linux machine. The Bebop 2 is based on the same architecture as the Bebop with a few noticeable changes, not the least being a much better quality GPS (UBlox GPS with a bigger antenna).
Warning
Making the changes described in this article will void your warranty! Parrot’s technical support will not help you with this hack or to recover your original software.
Warning
Hacking a commercial product is risky! This software is still evolving.
That said, it is almost always possible to recover a drone and members of the ardupilot dev team can likely help people hacking or recovering their Bebop on this google group.
Building ArduCopter for Bebop 2¶
Tip
You can skip this step if you just want to try out the (experimental) binary version.
The following steps show how to build a custom version of the Copter software for Bebop 2:
Install armhf toolchain¶
Install Parrot’s version of linaro arm-linux-gnueabihf toolchain that can be downloaded from here
Install it (the toolchain will be extracted in /opt)
sudo dpkg -i parrot-tools-linuxgnutools-2016.02-linaro_1.0.0-5_amd64.deb
Add the path to the toolchain to the PATH variable
export PATH=/opt/arm-2016.02-linaro/bin:$PATH
Download and compile ArduCopter¶
Clone ardupilot repository
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/ArduPilot/ardupilot.git cd ardupilot
Building the flight control firmware is nearly identical for building for the Pixhawk except the build command is:
./waf configure --board=bebop ./waf build
Uploading the Firmware¶
Mission Planner can now upload stable and custom versions of ardupilot to the Bebop2.
Instructions below are for the manual method of uploading
Install adb (android debug tool):
sudo apt-get install android-tools-adb
Connect to the Bebop2’s WiFi network (BebopDrone-XXXX).
Enable adb server by pressing the power button 4 times.
Connect to the Bebop’s adb server on port 9050:
adb connect 192.168.42.1:9050
If the previous command returns an error, try again (press the power button 4 times and retry).
Remount the system partition as writeable:
adb shell mount -o remount,rw /
Push the stripped arducopter binary to the Bebop2:
adb mkdir /data/ftp/internal_000/APM adb push arducopter /data/ftp/internal_000/APM/
Starting ArduPilot¶
Kill the regular autopilot:
adb shell kk
Launch Copter:
cd /data/ftp/internal_000/APM arducopter -A udp:192.168.42.255:14550:bcast -B /dev/ttyPA1 -C udp:192.168.42.255:14551:bcast -l /data/ftp/internal_000/APM/logs -t /data/ftp/internal_000/APM/terrain
Launch Copter at startup¶
As for Bebop, modify the init script /etc/init.d/rcS_mode_default. Comment the following line:
DragonStarter.sh -out2null &
Replace it with:
/data/ftp/internal_000/APM/arducopter -A udp:192.168.42.255:14550:bcast -B /dev/ttyPA1 -C udp:192.168.42.255:14551:bcast -l /data/ftp/internal_000/APM/logs -t /data/ftp/internal_000/APM/terrain &
Enable adb server by pressing the power button 4 times.
Connect to adb server as described before:
adb connect 192.168.42.1:9050
Re-mount the system partition as writeable:
adb shell mount -o remount,rw /
In order to avoid editing the file manually, you can download this one.
Save the original one and push this one to the bebop
adb shell cp /etc/init.d/rcS_mode_default /etc/init.d/rcS_mode_default_backup adb push rcS_mode_default /etc/init.d/
Sync and reboot:
adb shell sync adb shell reboot
Recovery¶
For recovery, you can use the same cable as the one used on Bebop, see here.
Remove the two screws using a torx T6 screwdriver
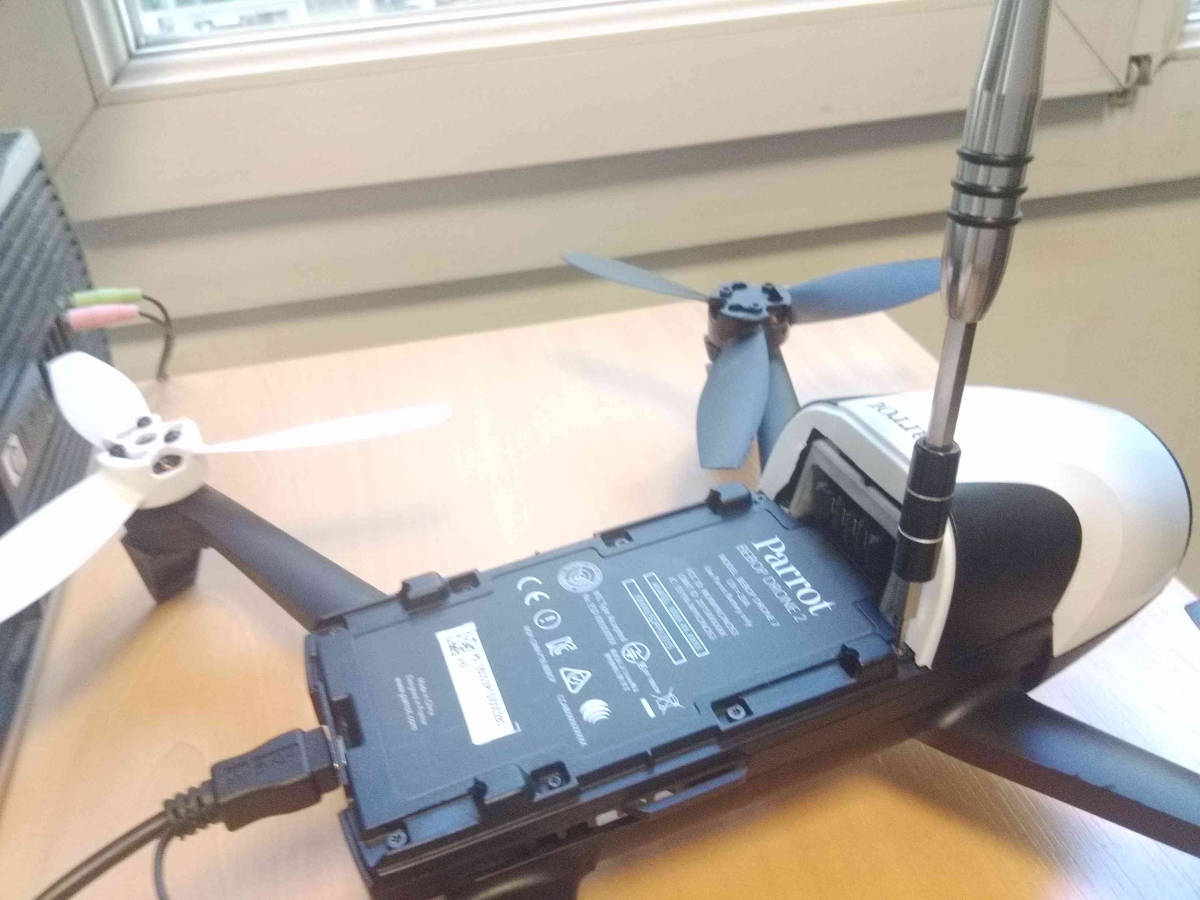

Remove the neck by pulling it towards the front of the Bebop
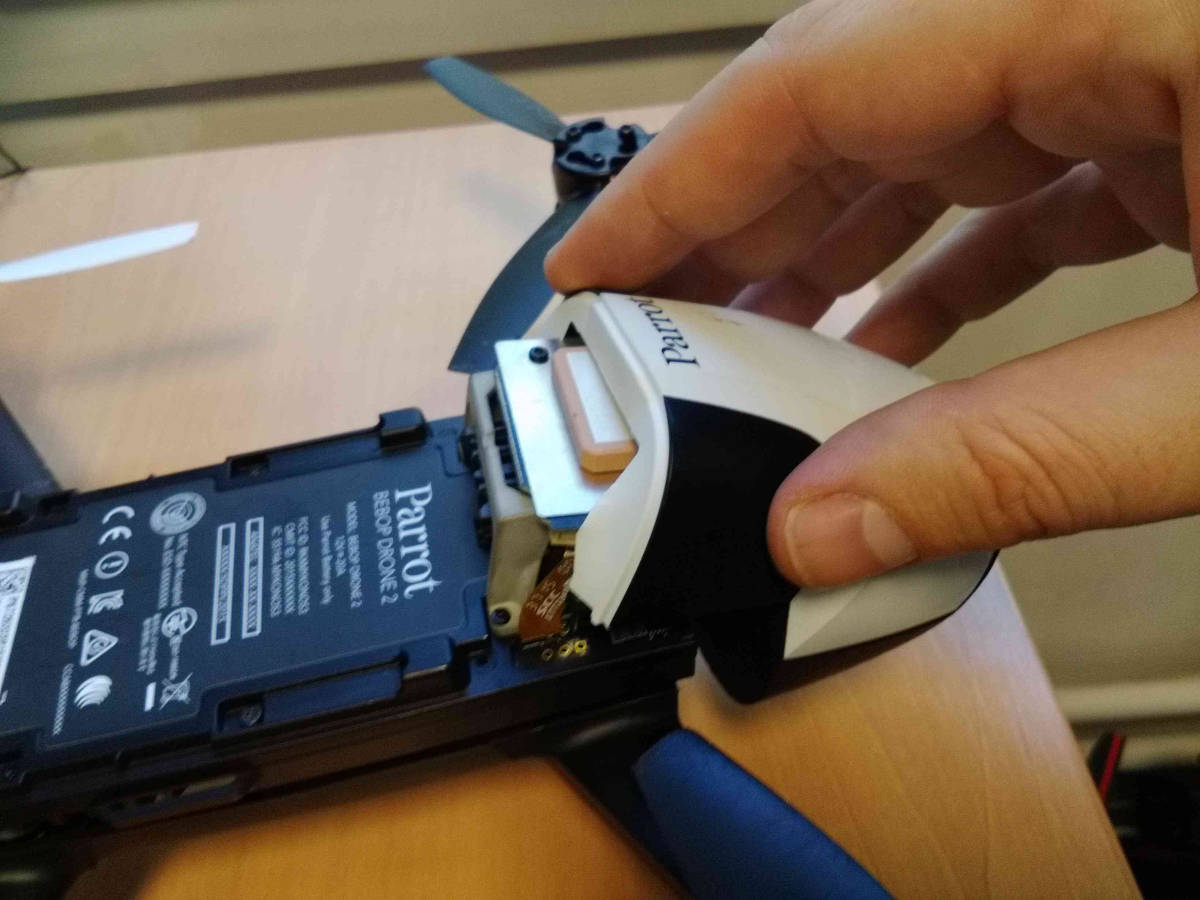

The UART connector is located on the right side
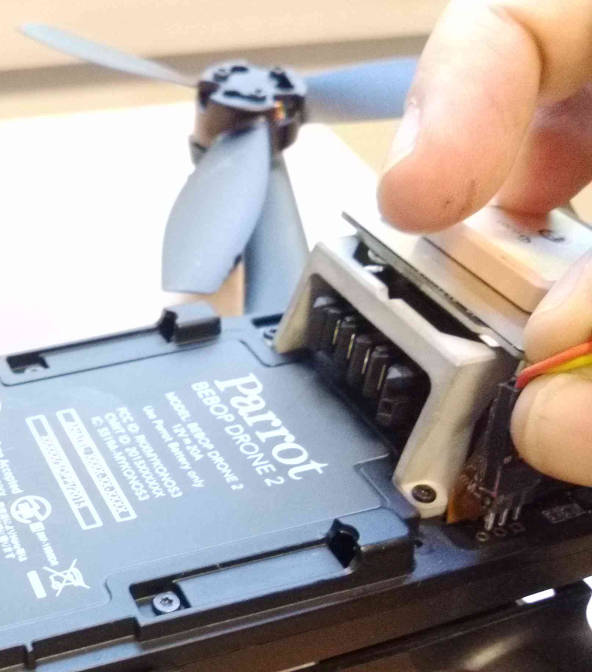
Plug the cable with the black wire at the front
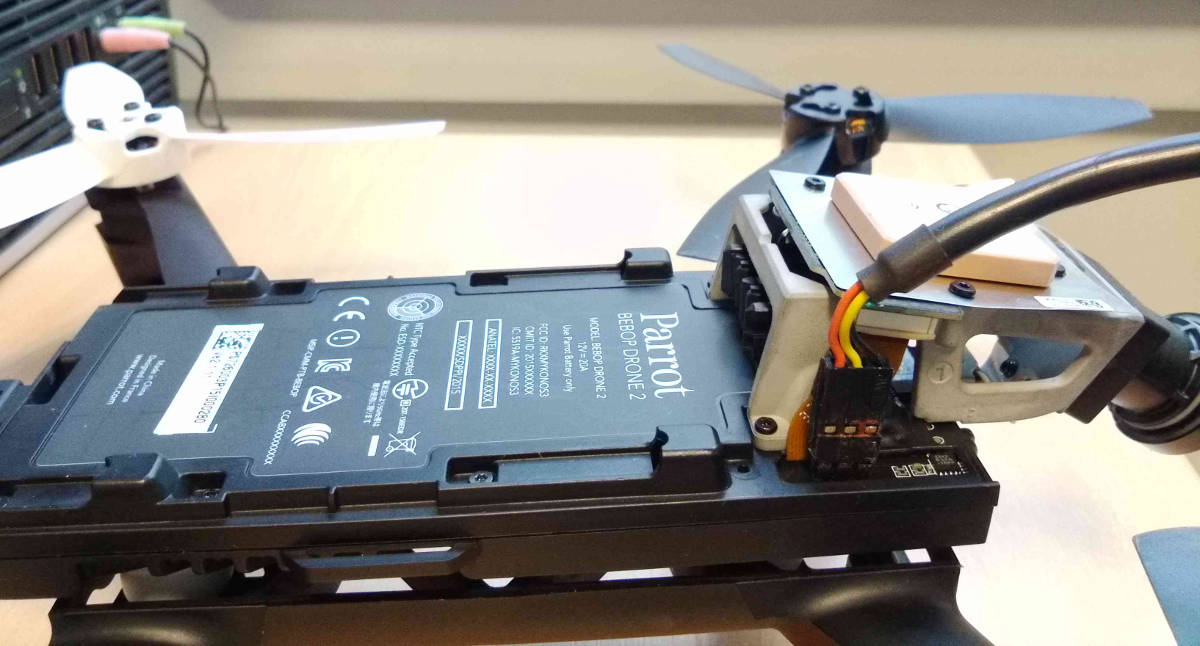

Connect to the bebop with the UART port using any terminal emulator
Copy the backup rcS file back to its place
mount -o remount,rw / cp /etc/init.d/rcS_mode_default_backup /etc/init.d/rcS_mode_default
Sync and reboot
sync reboot
Flying and RC over UDP¶
Flying and RC over UDP instructions are the same as the ones for Bebop
Basic configuration and frame parameters¶
The set of tuning parameters can be found here. These are not yet fully tuned for Bebop 2
In order to do the basic configuration and calibration, you can use any of the GCSs and perform:
Magnetometer Calibration
RC Calibration
Accelerometer Calibration
Additional information¶
The loiter mode quality is very good compared to the first Bebop because of the (much better) UBlox GPS. It is now safe to takeoff and land in the mode you want.
There is still no support for video yet and the optical flow and sonar are currently under development.
This is a good time to participate and help improve them!